Salts, moisture, plaster detachment: these are the effects of constant water presence. An interesting project carried out by Volteco in the last years showed the high impact of anticondensation technologies to mitigate temperature and humidity presence.
On other hand use of anti-condensation mortars in basement showed higher resistance to these phenomena proliferation and, not less important, higher indoor temperature as showed with termography technology.
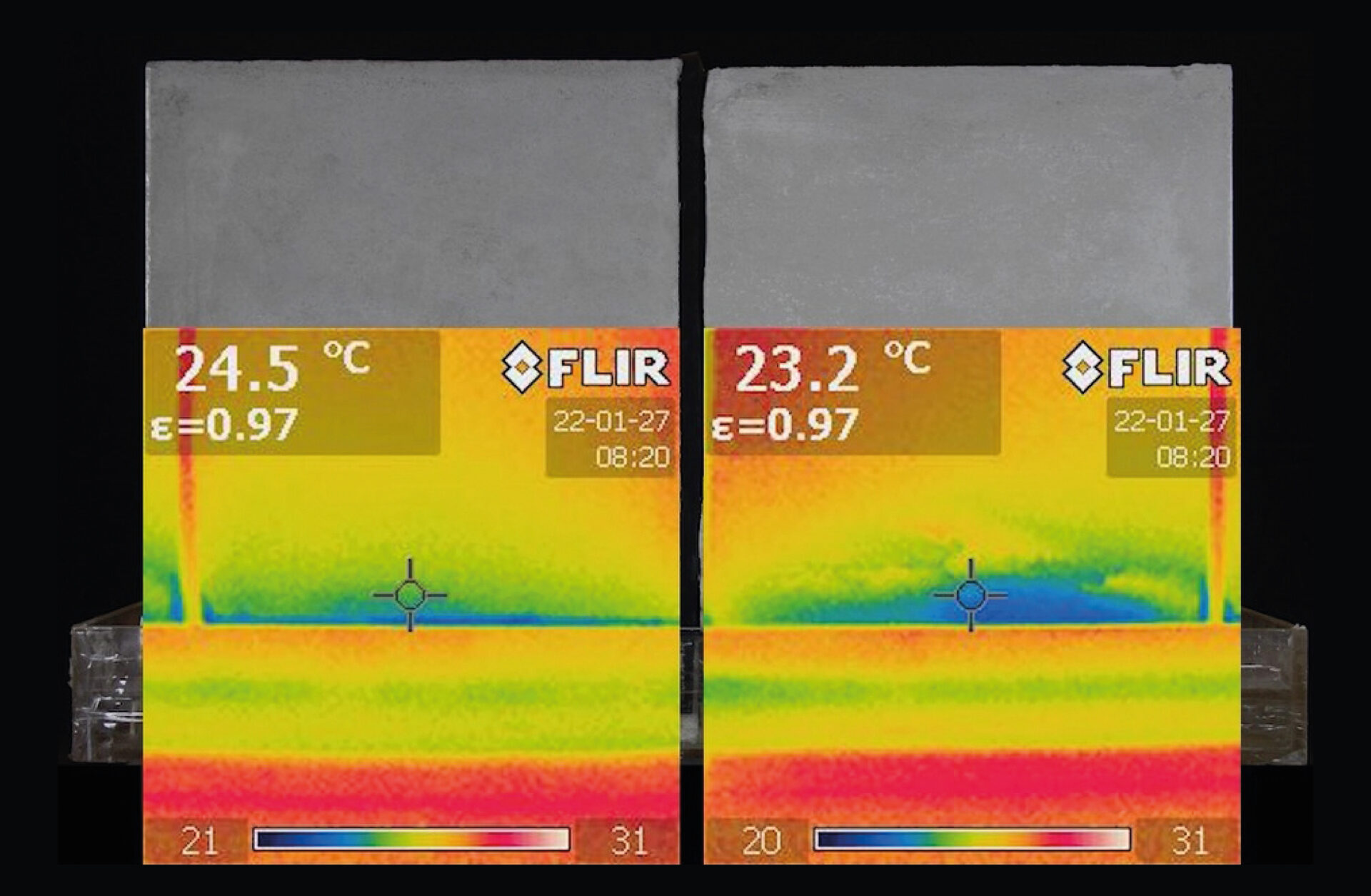
Is thermography reliable tool for basements monitoring and moisture control?
Thermography, also known as infrared thermography or thermal imaging, can be a reliable tool for assessing basement waterproofing, but as verified in several on site inspections, it has its limitations and should be used in combination with other diagnostic methods. Here’s a detailed look at the reliability and application of thermography in basement waterproofing:
PROs:
- non-invasive: thermography is a non-invasive technique, allowing for inspection without the need to damage the structure.
- real-time analysis: provides immediate results, enabling quick identification of potential problem areas.
- moisture detection: effective at detecting temperature differences caused by moisture presence, which often appears cooler than dry areas.
- comprehensive coverage: can scan large areas quickly, making it suitable for initial assessments of extensive basement spaces.
- hidden issues: can identify hidden issues such as leaks behind walls, under floors, or within ceilings that may not be visible to the naked eye.
CONs:
- surface-level detection: primarily detects surface temperature variations and may not accurately reflect issues deep within walls or floors or individuating real source of problem.
- ambient conditions: accuracy can be affected by ambient temperature and humidity conditions. Moisture signatures might be less distinct in certain environmental conditions.
- required expertise: interpretation of thermal images requires expertise to distinguish between different potential causes of temperature anomalies (e.g., moisture vs. insulation issues).
- complementary tool: best used as part of a multi-tool approach. Confirmatory methods such as moisture meters or destructive testing (e.g., core samples) might be necessary for definitive diagnosis.
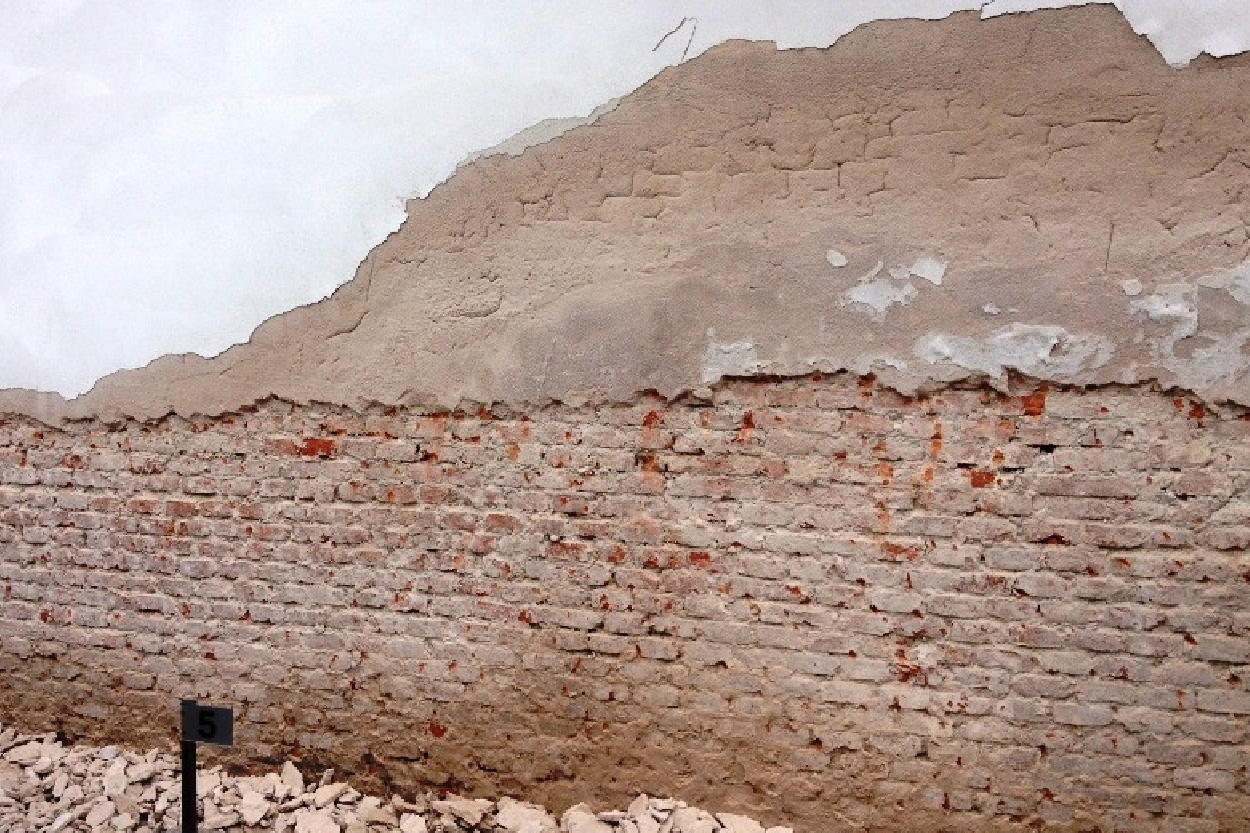
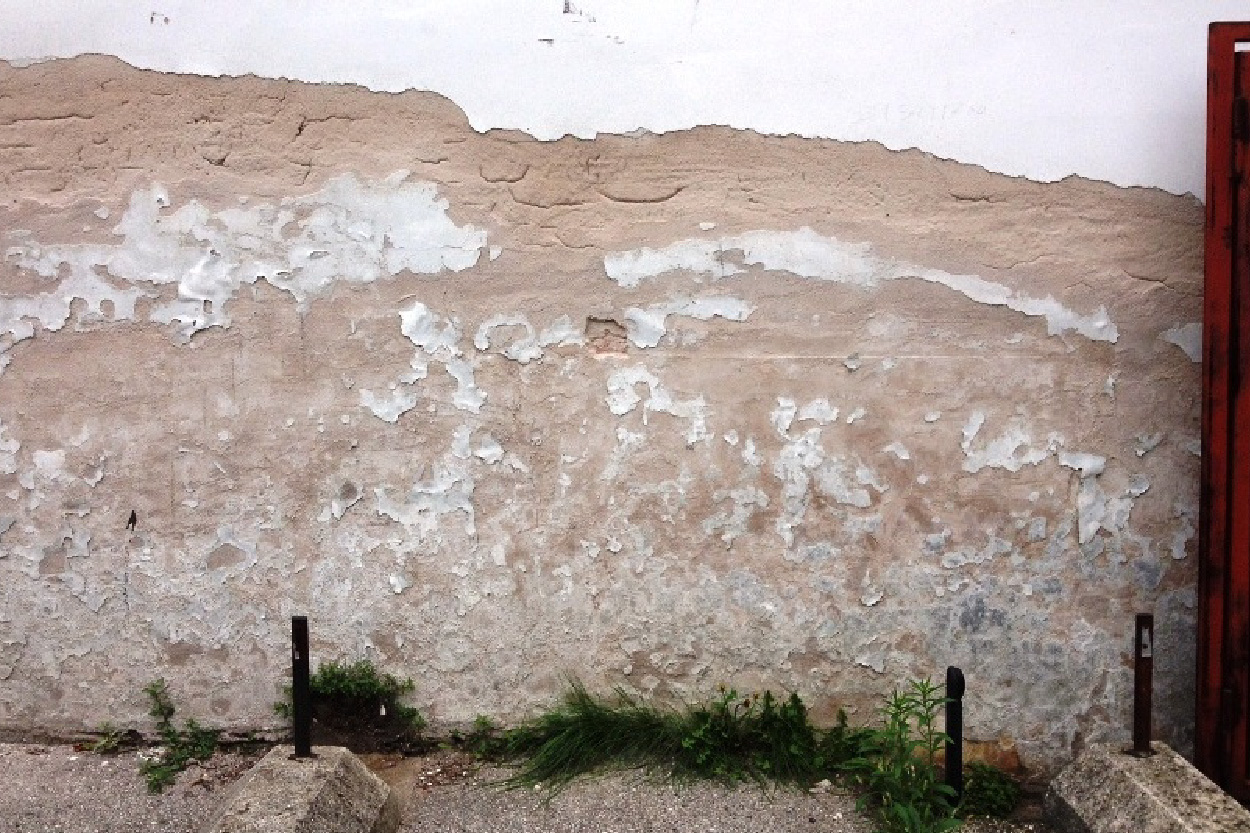


In this contest it is important to highlight other complementary Diagnostic Methods & tools
- moisture meters: to measure the actual moisture content in materials.
- visual inspections: to look for visible signs of water damage, mold, or mildew.
- destructive testing: in some cases, removing small sections of wall or flooring to directly inspect for moisture.
- hydrostatic pressure testing: assessing the pressure exerted by water in the surrounding soil.
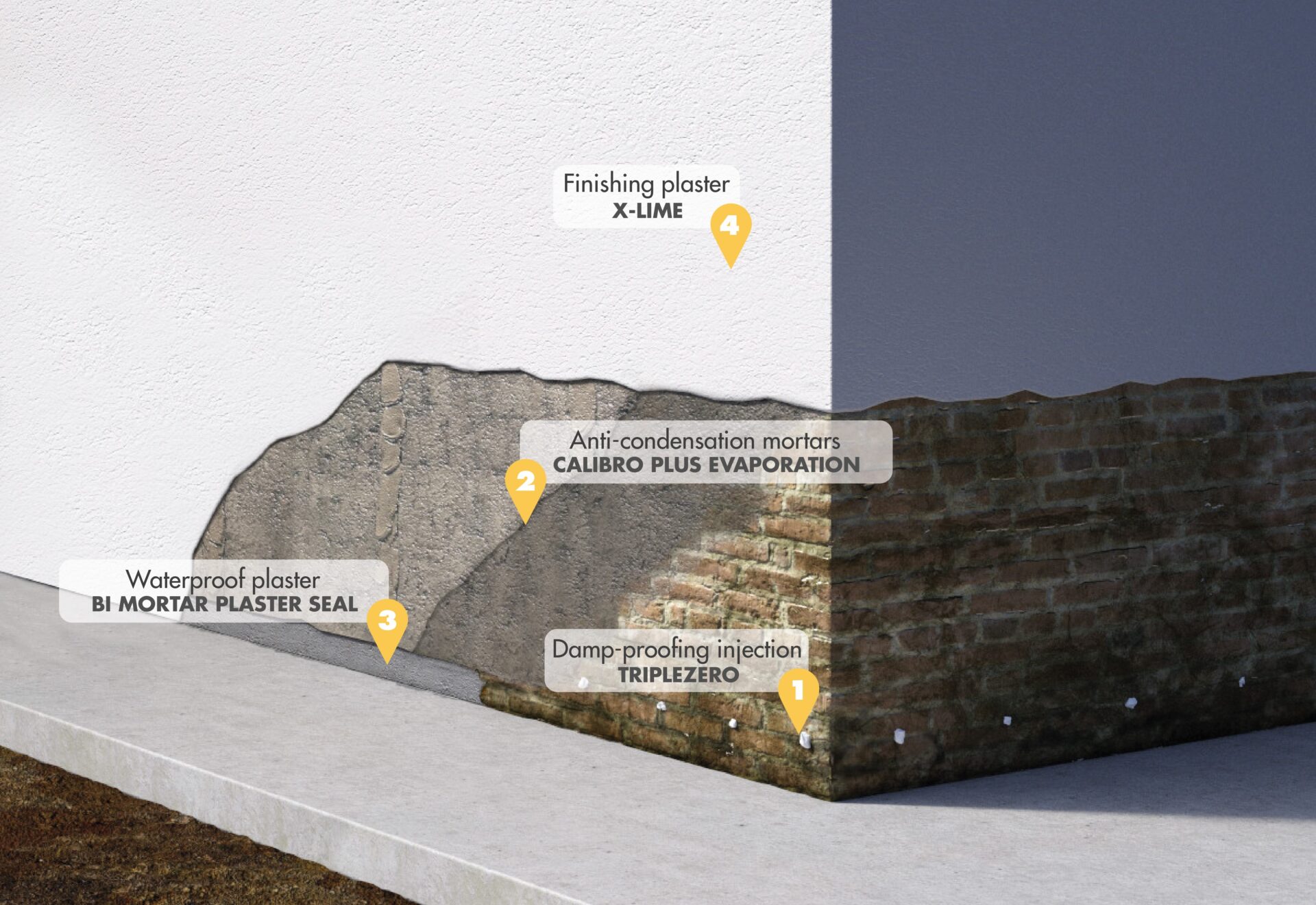

Discover our solutions for dehumidification and plaster repairing.
Are you interested in some practical applications of thermography?
Take a look at these interesting projects of historical buildings renovation
Dehumidification of damp walls – Castel Viscardo – Orvieto – TR – Italy | Volteco
Dehumidification of damp walls – San Pellegrino – Italy | Volteco




